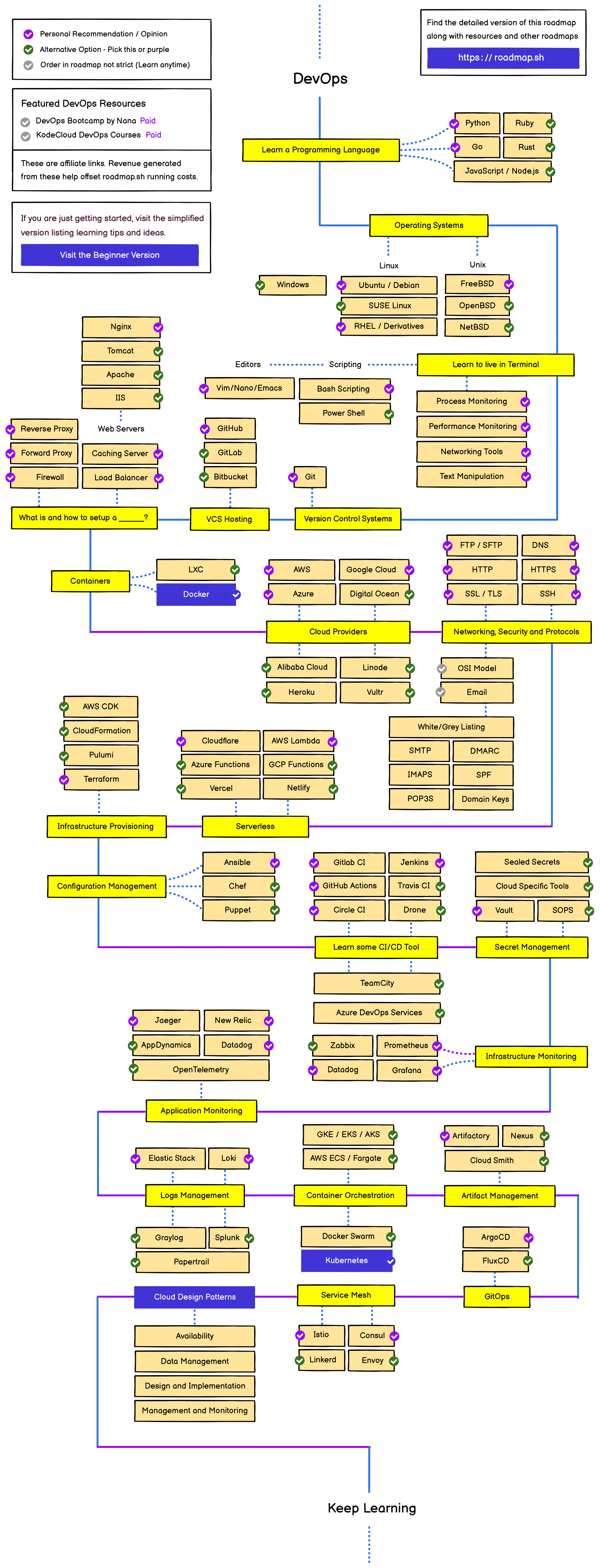
DevOps learning path and experience
Your Path to Becoming a DevOps Pro: From Foundational Knowledge to Advanced Automation 🚀
Embarking on the journey of DevOps can feel like navigating an intricate maze of technologies, platforms, and practices. Having worked through many of these steps, I’ve gathered experiences and insights that will guide you in mastering the DevOps landscape. Here’s a breakdown based on the detailed DevOps roadmap and a few personal touches from the field.
1. Learn a Programming Language 🖥️
Core Languages to Focus On:
- Python: My personal go-to for scripting and automation. It’s readable, versatile, and widely supported in DevOps tools.
- Bash: Essential for quick scripting and system-level tasks.
- JavaScript/Node.js: Useful for full-stack development scenarios.
Why This Is Important:
Programming helps you script automated tasks, build CI/CD pipelines, and troubleshoot applications. I often found Python invaluable for building custom scripts and integrating various tools seamlessly.
2. Master Operating Systems 🐧🪟
Start With:
- Linux (Ubuntu/Debian): The backbone of most DevOps environments.
Pro Tip:
Dive deep into system internals. Understanding how processes work, logging mechanisms, and file system structures are crucial, especially when deploying services or troubleshooting complex issues.
3. Live and Breathe the Terminal 💻
Skills to Hone:
- Editors: Get comfortable with
vim,nano - Scripting: Shell scripting is your Swiss Army knife for automating tasks and operations. GPT helps in this, but give simple and concise instruction
Personal Insight:
I still remember how mastering shell scripting helped me reduce deployment times by automating repeatable tasks like log rotation and server health checks.
4. Version Control Systems (VCS) 📚
Tool of Choice:
- Git: The industry standard for version control. Learning Git deeply (rebasing, merging, branching strategies) has been a game-changer in collaborating with teams efficiently.
VCS Hosting:
- GitHub: In my experience, GitHub Actions has been particularly effective for automating CI/CD workflows directly in the repository.
5. Containers & Orchestration 🐳
Get Started With:
- Docker: The starting point for containerization. Build, ship, and run applications consistently.
- Kubernetes (K8s): The king of container orchestration. Understanding its architecture, pod scheduling, and networking models are crucial.
First-Hand Takeaway:
Containers are like modern-day development magic. Moving from Docker basics to deploying multi-service applications on Kubernetes significantly elevated my project delivery speed and consistency.
6. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) 🌍
First Layer Automation:
- Terraform: An essential tool for defining and provisioning infrastructure. It’s declarative, scalable, and widely supported across cloud providers. I learned that versioning infrastructure code is just as important as application code. It allows teams to revert changes and understand infrastructure drift. Understand vault is also important(how insecure saving things in env variables)(Use Terraform to automate deployment of aws vm as testing)
Second Layer Automation:
- Ansible: My favorite for configuration management. Unlike Terraform, which is primarily about infrastructure provisioning, Ansible steps in for post-deployment configurations, state management, and orchestration.
Field Insight:
Using Terraform to provision cloud infrastructure and Ansible to configure and manage the software environment on top of it creates a powerful, automated workflow. I once automated an entire staging environment setup with Terraform (infrastructure) and Ansible (application deployment), saving hours of manual intervention.
7. CI/CD Pipelines 🔄
Tools to Explore:
- GitHub Actions: Start with a simple pipeline to automate tests and builds. Then scale up to complex deployments.(You can explore Jenkins as well(hot question in vulnerable box))
What Worked for Me:
Automating build, test, and deploy stages helped teams shift to a true DevOps model with continuous feedback loops. I enjoyed experimenting with GitLab CI/CD due to its native GitLab integration and flexible pipeline configurations.
8. Monitoring & Logging 📊
Key Tools:
- Prometheus & Grafana: Go-to for infrastructure monitoring. Setting up custom metrics with Prometheus and visualizing them in Grafana gave me critical insights into application performance.
- Elastic Stack (ELK): For comprehensive log analysis.
9. Cloud Providers ☁️
Must-Know Platforms:
- AWS: With services like EC2, S3, and Lambda, AWS is dominant. I highly recommend hands-on practice using the AWS Free Tier.
10. Advanced Topics 🧠
Explore:
- Service Mesh (e.g., Istio, Linkerd): To manage microservices communication.
- GitOps: Tools like ArgoCD bring declarative configurations to deployments.
- Security Practices: Emphasize secret management with Vault or SOPS and learn about secure coding practices.
Final Advice:
The DevOps landscape is vast and always evolving. Keep learning, stay curious, and don’t hesitate to dive deep into areas you find challenging. Build projects, contribute to open source, and create your own labs to reinforce what you learn. The hands-on experience is your best teacher. Devopsdirective is a great course on youtube, the courses isn’t complete yet, but worth watching(Terraform, Docker, Part of Kubernetes available for now).
Happy learning, and remember to automate wherever you can! 🚀🔧
Above blog is generated with the help of GPT XD